Green Energy Today
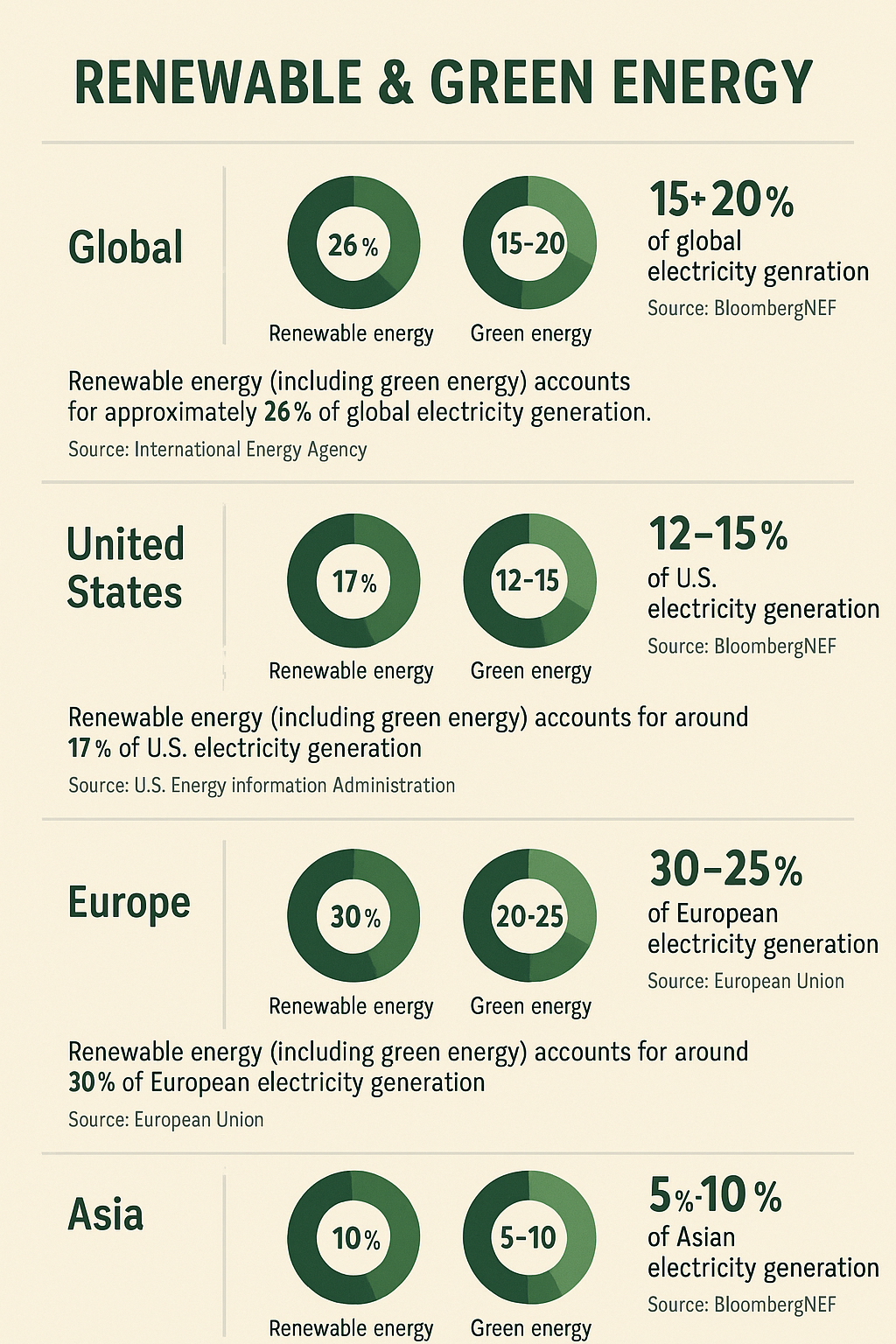
Information about where Green Energy is today in terms of capacity deployed in the United States, Europe, Asia, and the rest of the world.
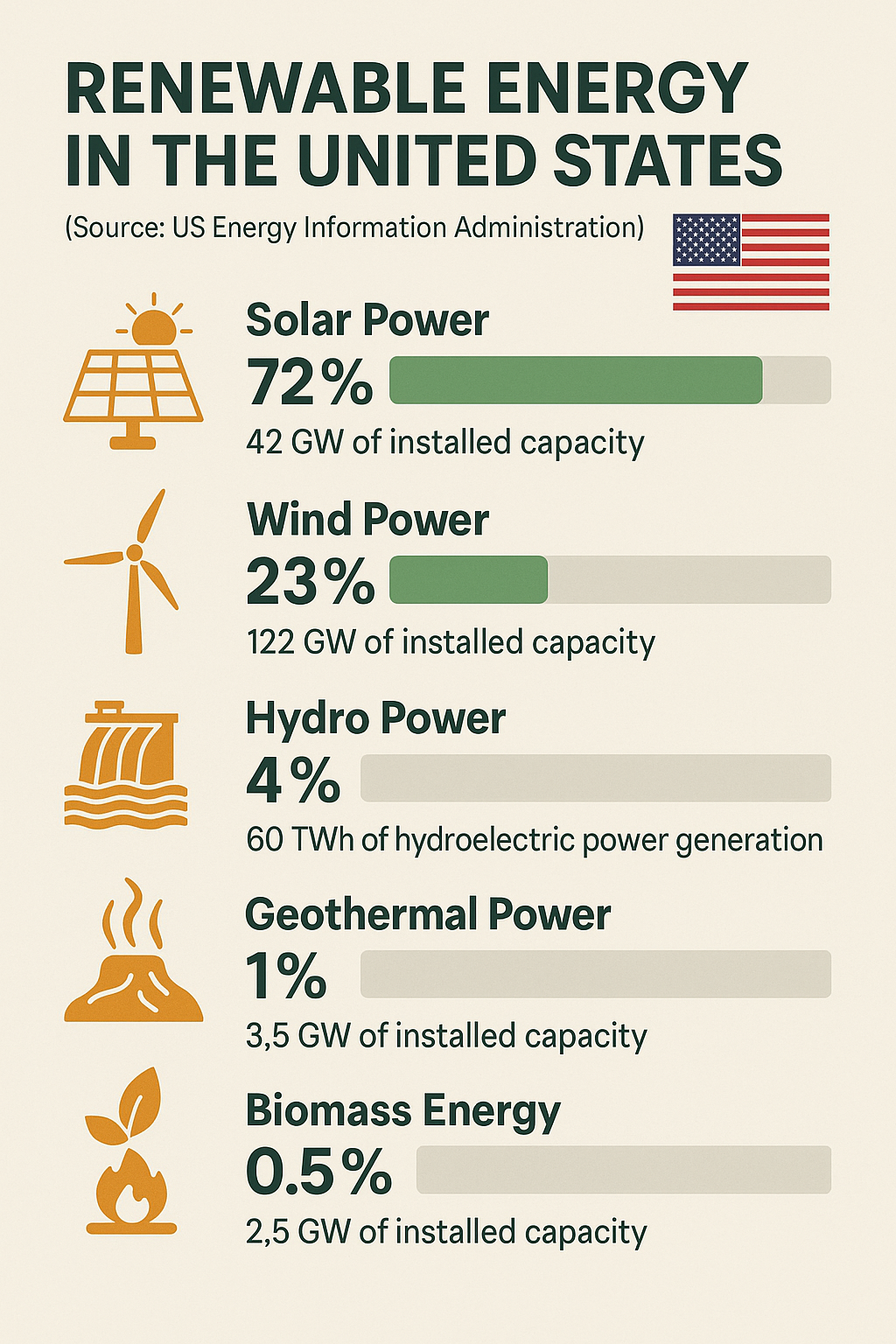
The most popular form of Green Energy today is Solar Energy with an estimated 700 GW (gigawatts) of annual capacity globally.
Here's a rough estimate of the global capacity for each of these forms of green energy:
Solar Energy: 700 GW (gigawatts)
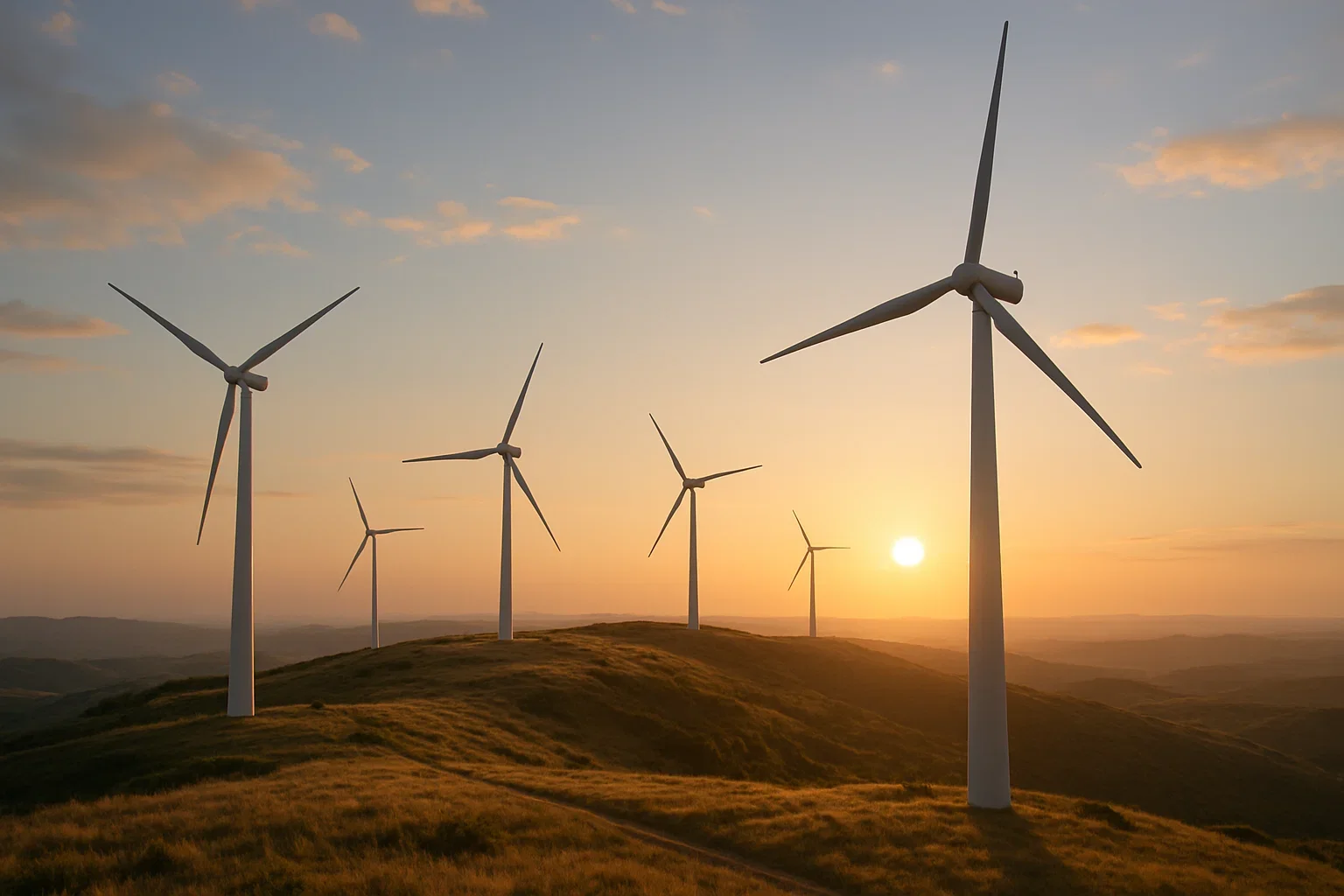
Wind Energy: 600 GW
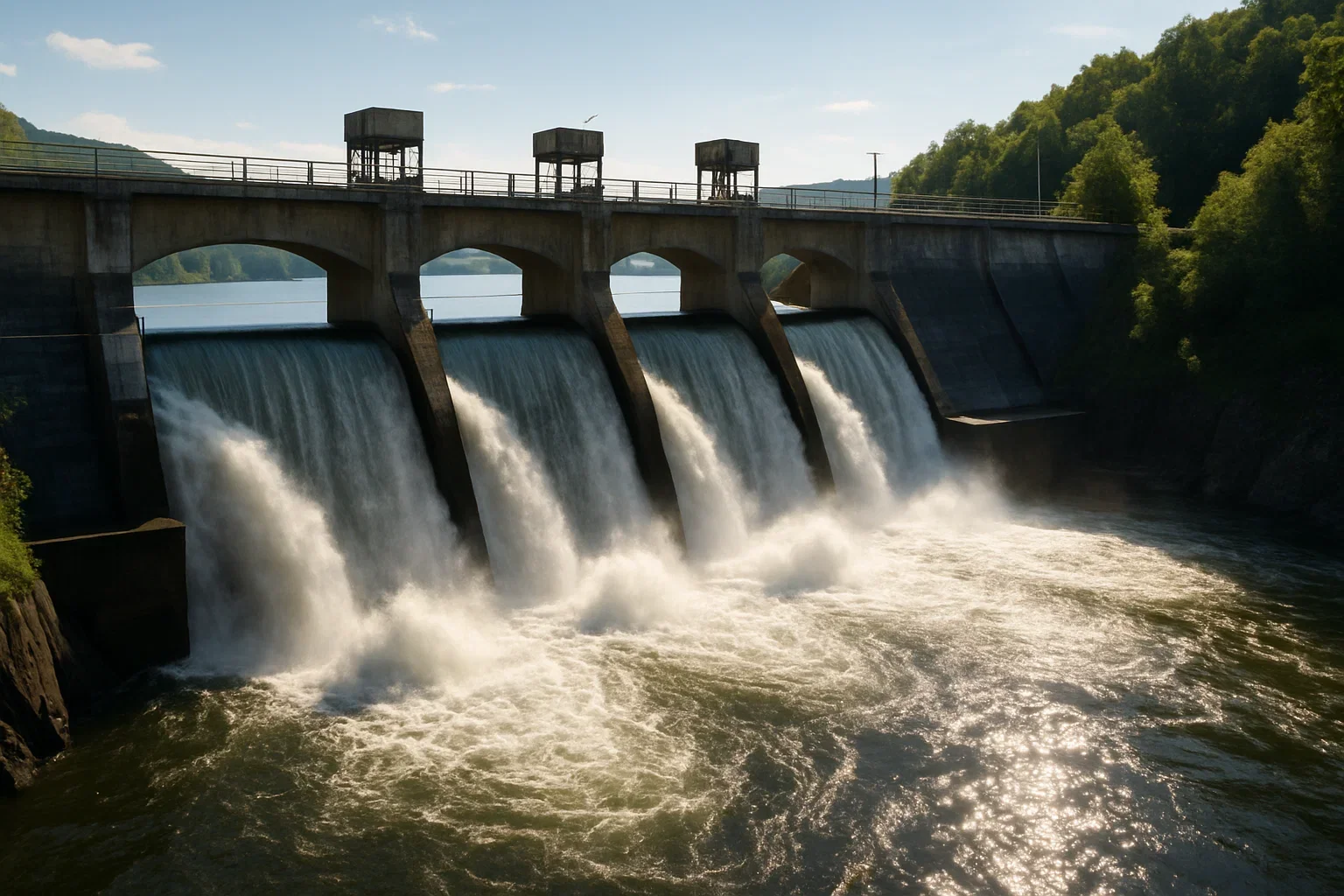
Hydro Energy: 1,200 TWh (terawatt-hours)
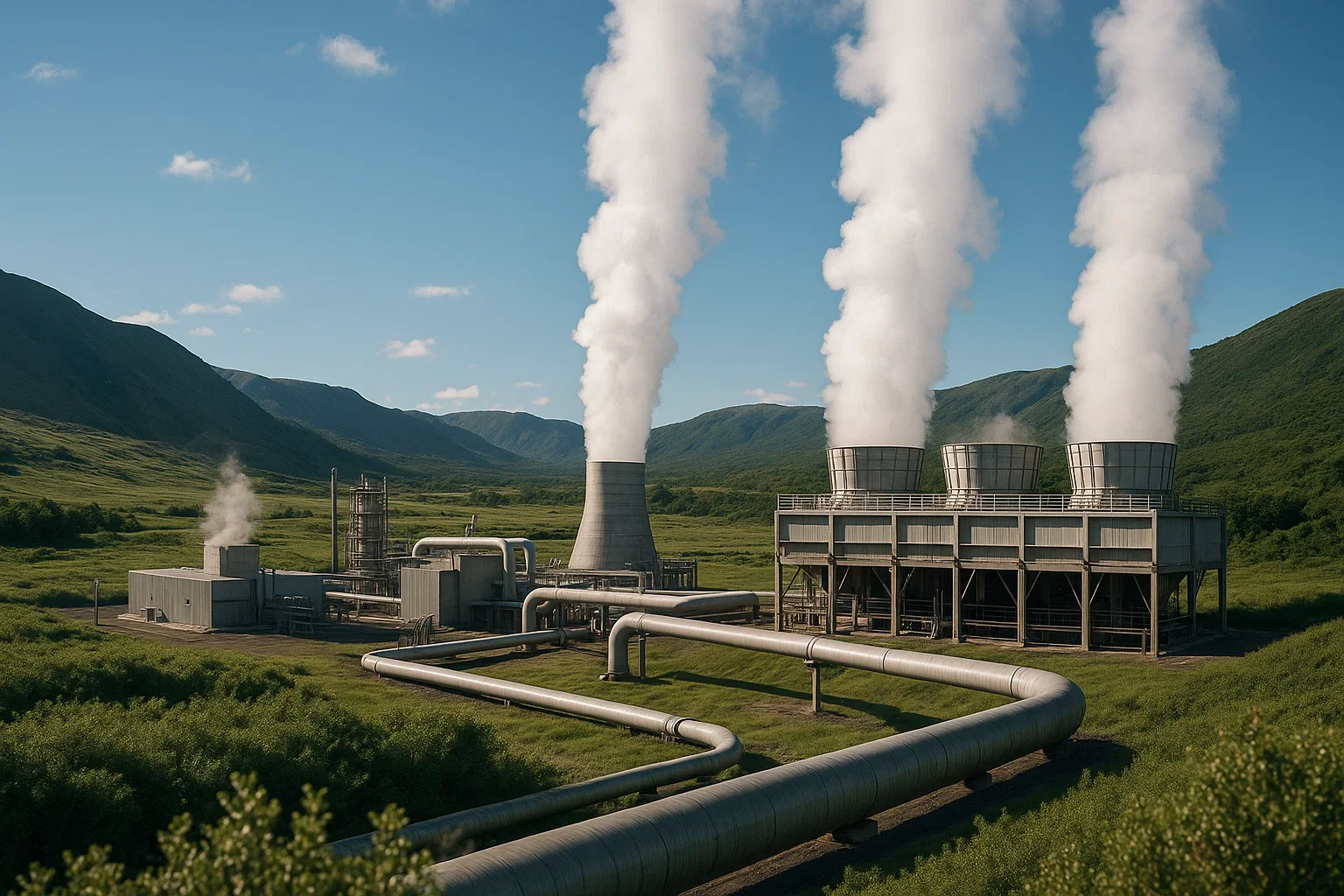
Geothermal Energy: 12 GW
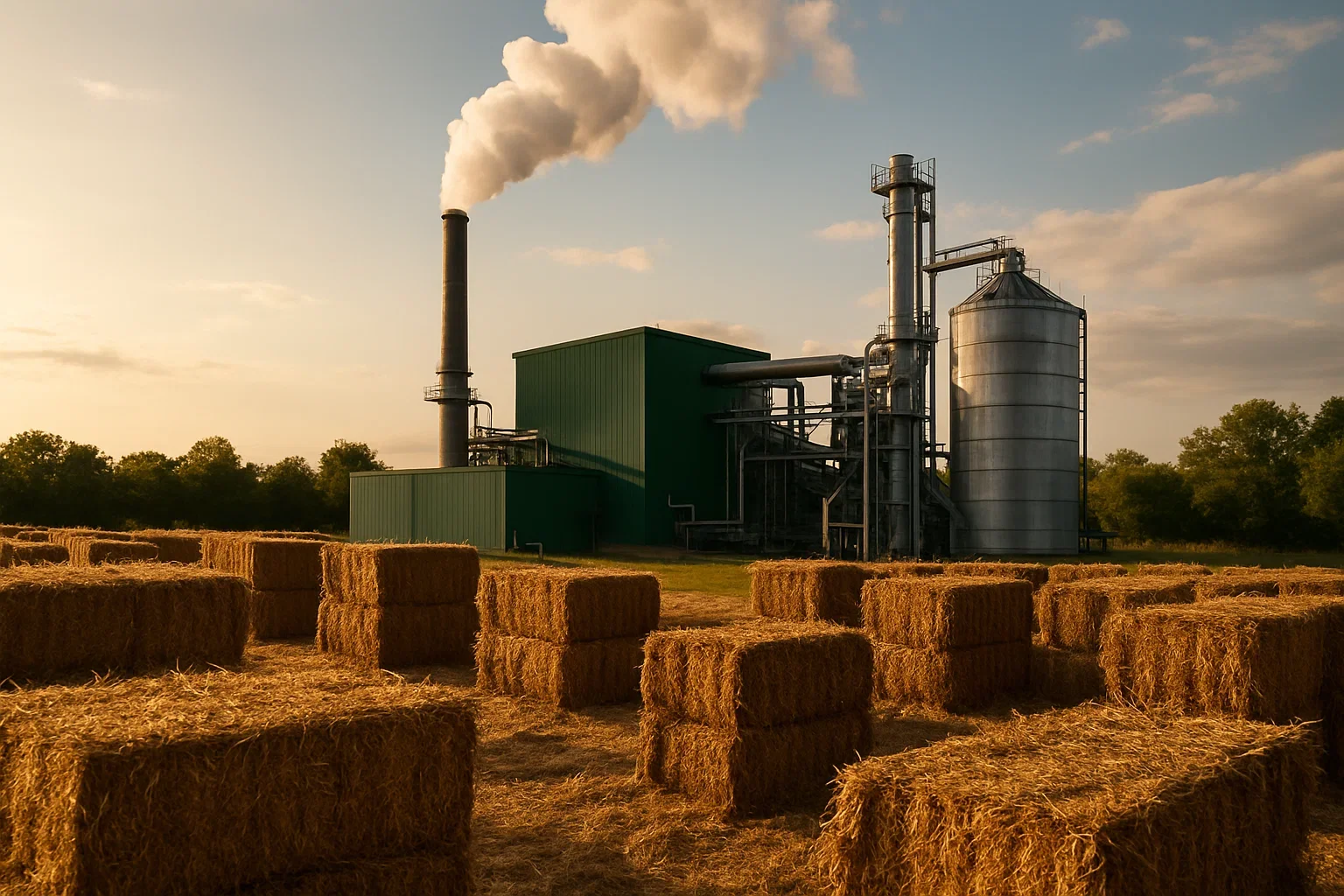
Biomass Energy: 60 GW
1 GW is equal to approximately 8.76 TWh
These numbers are constantly changing as new projects come online and technology improves.
Sources: BloombergNEF, Wood Mackenzie, Global Wind Energy Council (GWEC), International Energy Agency (IEA)
Green Energy Explained
A definition of green energy and an overview of the different types of renewable energy sources that are being harnessed.
Green energy, also known as renewable energy or sustainable energy, refers to the production of energy from natural resources that are replenished at a rate that is comparable to or greater than the rate at which they are consumed. Due to the rate of replenishment outpacing consumption, the supply is limitless.
Now looking at the term “green energy” and the definition refers to two distinct concepts: the meaning of the words "energy" and "green."
What does "Energy" mean?
In this case, "energy" specifically refers to electricity. So, green energy is essentially renewable electricity.
What does "Green" mean?
Now, when we say "green," we're talking about something that's renewable, sustainable, and environmentally friendly. In the context of energy, green means that the source of electricity is not dependent on finite resources like fossil fuels, but rather relies on natural processes that can be replenished over time.
So, what does it mean to have "Green Energy"?
In simple terms, green energy refers to the production and consumption of renewable electricity, which is generated from natural sources such as:
Solar Power: Electricity produced by converting sunlight into electrical energy.
Wind Power: Electricity generated from the kinetic energy of wind using turbines.
Hydro Power: Electricity produced by harnessing the energy of moving water, like rivers or ocean tides.
Geothermal Power: Electricity generated from the heat of the Earth's core.
Biomass Power: Energy is generated from organic matter such as wood, agricultural waste, and even wastewater, producing heat or electricity.
The benefits of green energy include:
Renewable and Sustainable: Green energy sources are replenished naturally, making them a sustainable option for future generations.
Reduced Emissions: Green energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
Energy Independence: Green energy can provide energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
Job Creation: The green energy industry is creating new job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
In summary, when we talk about "green energy," we're referring to the production and consumption of renewable electricity generated from natural sources, which is a crucial step towards a more sustainable future for our planet!