Meat Eating and The Environment
As we explore the effects of our food choices on the environment, it's essential to consider the significant role that meat consumption plays in contributing to climate change.
Livestock Farming and Climate Change
According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), livestock farming is a significant contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, accounting for around 14.5% of global emissions. This is largely due to the production of meat, dairy products, and other animal-derived foods, which requires vast amounts of land, water, and energy.
Meat Consumption in Different Regions
The average adult in the US consumes around 223 pounds of meat per year, with beef being the most popular type. In Europe, the average person consumes around 133 pounds of meat per year, while in Asia, it's around 100 pounds.
Dietary Impacts on the Environment
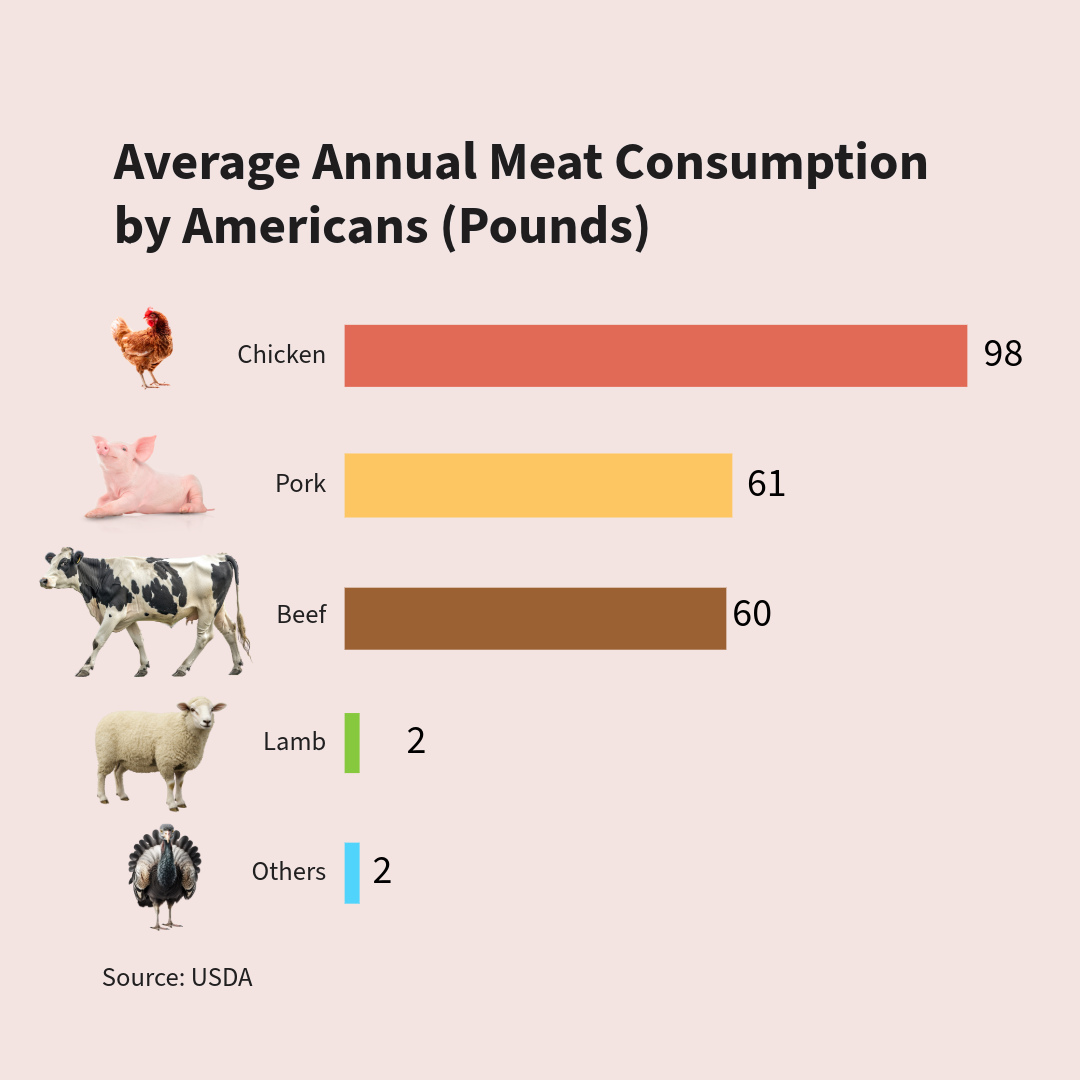
The effects of eating pork, chicken, and other meats on the environment are significant. Here's data on the average American’s annual meat consumption:
Cutting Out the Middle-Man: Vegetarian Alternatives
One way to reduce the environmental impact of meat consumption is to adopt a vegetarian diet. This can be achieved by cutting out the middle-man and feeding grains and vegetables directly to humans, rather than using them as feed for livestock. By doing so, we can reduce the demand for animal products and promote more sustainable agriculture practices.
As we explore the impact of our food choices on the environment, it's essential to consider the strategies for reducing the carbon footprint of our daily food choices. Here are some other effective ways to make a positive difference:
Choose Plant-Based Options: Focusing on plant-based diets can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture and transportation.
Opt for Locally Sourced Foods: Supporting local farmers and purchasing locally grown produce reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
Select Organic or Regenerative Produce: Choosing organic or regenerative produce promotes sustainable farming practices, which can help sequester carbon in soils and promote biodiversity.
Consume Less Meat: Reducing meat consumption or choosing plant-based alternatives can decrease the environmental impact of animal agriculture.
Reduce Food Waste: Planning meals, using up leftovers, and composting food waste can minimize the energy required for production, processing, and transportation.
Use Eco-Friendly Packaging: Choosing products with minimal packaging, biodegradable packaging, or reusable containers can reduce waste and pollution.
Shop in Bulk: Purchasing items like grains, nuts, and dried fruits in bulk reduces packaging waste and supports sustainable agriculture.
Support Sustainable Seafood: Choosing seafood from well-managed fisheries or aquaculture operations can help promote marine ecosystems and reduce bycatch.
Explore Alternative Protein Sources: Incorporating alternative protein sources like insects, algae, or plant-based alternatives into your diet can decrease the environmental impact of animal agriculture.
Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home using fresh ingredients can reduce packaging waste, support local economies, and promote sustainable food systems.
Additional Tips
Eat Seasonally: Consuming produce in season reduces the energy required for transportation and storage.
Avoid Single-Use Plastics: Refusing single-use plastics like straws, bags, and containers can minimize marine pollution and waste.
Support Sustainable Agriculture: Encouraging sustainable agriculture practices through certifications like USDA Organic or Fairtrade can promote environmentally friendly farming methods.
Get Involved in Your Community: Participating in local food initiatives, advocating for policy changes, and educating others about the importance of sustainable food choices can drive positive change.
By implementing these strategies, we can make a significant impact on reducing the carbon footprint of our daily food choices and contributing to a more sustainable food system.